TL;DR
An HTML 301 redirect is not a direct HTML feature but refers to the use of the HTTP 301 "Moved Permanently" status code to permanently forward one URL to another. It signals to browsers and search engines that a page's location has changed for good. This process is critical for SEO, as it transfers the original page's ranking authority and link equity to the new URL, ensuring a seamless user experience and preserving search visibility.
What Is a 301 Redirect and Why Is It Crucial for SEO?
A 301 redirect is an instruction sent from a web server to a browser, indicating that a requested resource has been permanently moved. As defined by authoritative sources like the MDN Web Docs, the HTTP 301 Moved Permanently response status code is the standard, server-level method for this task. When a browser receives this code, it automatically requests the new URL provided in the server's response. For users, this transition is nearly instantaneous and often goes unnoticed.
The true power of a 301 redirect lies in its impact on Search Engine Optimization (SEO). When you move a page, you don't want to lose the valuable search ranking and authority it has accumulated. According to Google's official documentation, a 301 redirect acts as a strong signal that the new page should be considered the canonical version. This prompts search engines to transfer the ranking signals—often called "link equity" or "link juice"—from the old URL to the new one. Without a proper redirect, the new page would have to build its authority from scratch, and links pointing to the old page would lead to a broken (404 Not Found) experience.
Common scenarios where a 301 redirect is essential include migrating your entire website to a new domain, switching from HTTP to the more secure HTTPS protocol, consolidating duplicate content, or simply changing the URL structure of your pages. In each case, the 301 redirect ensures that both users and search engine crawlers are seamlessly guided to the correct, current location, preserving your site's hard-earned SEO value.
It's vital to distinguish a 301 redirect from its temporary counterpart, the 302 redirect. While both forward users to a new page, they send very different signals to search engines. A 301 says the move is permanent, while a 302 says it's temporary, meaning the original URL should remain indexed. Using the wrong one can have negative SEO consequences.
| Feature | 301 Redirect (Moved Permanently) | 302 Redirect (Found/Temporary) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Indicates a permanent move. The old URL is no longer valid. | Indicates a temporary move. The old URL will be used again. |
| SEO Impact | Passes most link equity and ranking power to the new URL. Search engines update their index to the new URL. | Does not pass significant link equity. Search engines keep the original URL indexed. |
| Common Use Cases | Domain changes, switching to HTTPS, permanent page moves, fixing broken links. | A/B testing, running short-term promotions, maintenance, location-based forwarding. |
How to Implement a 301 Redirect: Code-Based Methods
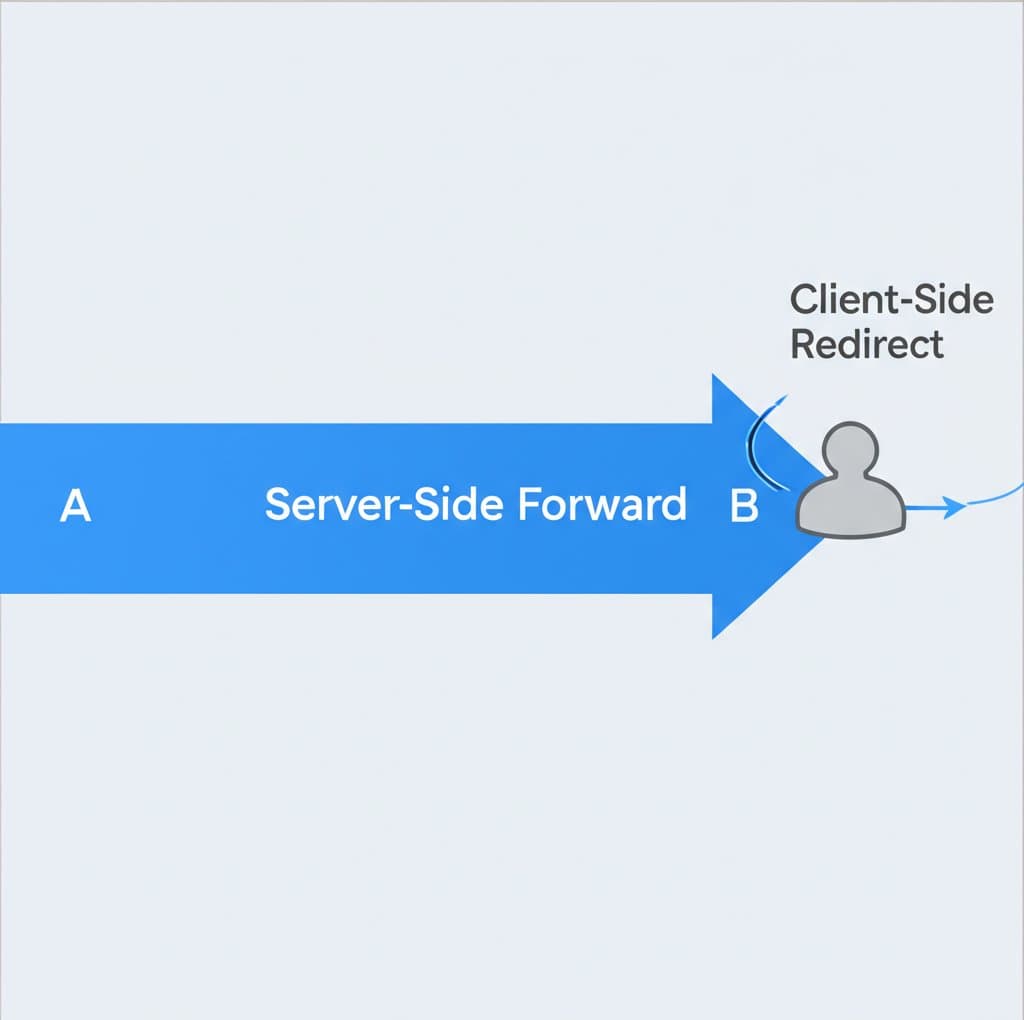
Implementing a 301 redirect can be done through several methods, but it's important to distinguish between server-side redirects (the recommended approach) and client-side redirects. A true 301 redirect is handled at the server level, meaning the server sends the 301 status code before the original page even loads. Client-side methods, like those using HTML or JavaScript, are executed by the user's browser after the original page has started loading and are generally less effective for SEO.
The most common and SEO-friendly method is configuring the redirect on your server, typically through the .htaccess file on an Apache server. This file allows you to write rules that control server behavior. To redirect a single page, you would add a line like this:
Redirect 301 /old-page.html https://www.yourwebsite.com/new-page.html
While often referred to as an "HTML 301 redirect," a true 301 cannot be set directly in an HTML file. However, a similar client-side effect can be achieved using the HTML meta refresh tag. As explained by Conductor, this method instructs the browser to load a new page after a set time. For an instant redirect that Google often interprets as a permanent one, you would place this in the <head> section of your HTML:
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0; URL='https://www.yourwebsite.com/new-page.html'" />
Another client-side option is using JavaScript to change the browser's location. This is generally the least recommended method for SEO, as it depends on the browser successfully executing the script, which search crawlers might not always do reliably.
<script> window.location.href = "https://www.yourwebsite.com/new-page.html"; </script>
Pros and Cons of Redirect Methods
- .htaccess (Server-Side)
- Pros: The most SEO-friendly method. It's fast, efficient, and sends a clear 301 signal to search engines, ensuring maximum link equity transfer.
- Cons: Requires access to server configuration files, which may be intimidating for non-technical users. Incorrect syntax can cause site-wide errors.
- HTML Meta Refresh (Client-Side)
- Pros: Easy to implement for users without server access. Can be added directly to an HTML file.
- Cons: Slower user experience because the original page must load first. According to Semrush, it passes less link equity than a server-side redirect and can be confusing for search engines.
- JavaScript (Client-Side)
- Pros: Offers flexibility for complex conditional redirects.
- Cons: Least reliable for SEO. If a search engine crawler has JavaScript disabled or rendering fails, the redirect will not be seen.
For optimal SEO and user experience, always use a server-side 301 redirect via .htaccess or your server's equivalent whenever possible.
Implementing 301 Redirects in Popular Platforms
For many website owners, editing server files like .htaccess is not a practical option. Fortunately, most modern Content Management Systems (CMS) and website builders provide user-friendly interfaces to manage 301 redirects without writing a single line of code. These tools handle the server-level configuration behind the scenes, making the process accessible to everyone.
In WordPress, the most popular CMS, 301 redirects are typically managed through plugins. Popular SEO plugins like Yoast SEO (Premium) or Rank Math include a built-in redirect manager. There are also dedicated plugins like Redirection that offer advanced features for creating and tracking redirects. The process usually involves a simple interface where you enter the old URL (the source) and the new URL (the destination).
Here are the general steps for using a WordPress redirection plugin:
- Install and activate a redirection plugin from the WordPress plugin directory.
- Navigate to the plugin's settings page, often found under the "Tools" or "Settings" menu in your WordPress dashboard.
- Find the section for adding a new redirect.
- In the "Source URL" field, enter the path of the old page you want to redirect (e.g.,
/old-blog-post). - In the "Target URL" field, enter the full URL of the new page (e.g.,
https://www.yourwebsite.com/new-blog-post). - Ensure the redirect type is set to 301 (Permanent) and save your changes.
Website builders like Wix and Shopify also have integrated redirect managers. In Wix, for example, you can find the "SEO Tools" section in your site's dashboard, which contains a URL Redirect Manager. The process is similar: you specify the old URL and the new destination URL, and the platform takes care of the rest.
While you focus on the technical aspects of SEO like redirects, it's also important to maintain a steady flow of high-quality content. For marketers and creators looking to streamline their workflow, an AI-powered tool can be a game-changer. For example, platforms like BlogSpark can help generate engaging, SEO-optimized articles, freeing up your team to focus on broader strategy and technical site health.
Using a platform's built-in tool or a trusted plugin is almost always preferable to manual methods for the average user. It reduces the risk of human error, provides an organized log of all your redirects, and makes the process of maintaining a healthy site structure much more manageable.
Troubleshooting Common 301 Redirect Errors
While 301 redirects are a powerful tool, incorrect implementation can lead to significant SEO and user experience problems. Two of the most common errors are redirect chains and redirect loops. Understanding how to identify and fix these issues is a critical part of website management.
A redirect chain occurs when one URL redirects to another, which then redirects to a third, and so on (e.g., Page A → Page B → Page C). Each step in the chain adds latency, slowing down the page load time for users. For search engines, it wastes crawl budget and can dilute the link equity being passed, as some value may be lost at each "hop." The best practice is to always redirect an old URL directly to its final destination, bypassing any intermediate steps.
A redirect loop is an even more serious problem where a URL redirects to another URL that, in turn, redirects back to the original (e.g., Page A → Page B → Page A). This creates an infinite loop that prevents the browser from ever loading a page. Users will see an error message like "ERR_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS," and search engine crawlers will abandon the request, unable to index the content. Loops are often caused by conflicting redirect rules in your .htaccess file or CMS plugin.
To diagnose and resolve these issues, follow this troubleshooting checklist:
- Use an Online Redirect Checker: Tools like Redirect Checker or What's My DNS provide a visual map of the redirect path. Enter your starting URL, and the tool will show you every hop it takes to reach the final destination. This is the quickest way to spot a chain or a loop.
- Inspect Your
.htaccessFile: If you manage redirects manually, carefully review your.htaccessfile for conflicting or outdated rules. Look for rules that might be targeting the same URL or creating a circular pattern. Always back up the file before making changes. - Check Your CMS Plugin Settings: If you use a plugin for redirects, review its configuration. Ensure there are no duplicate or contradictory entries. Some plugins have built-in error checking that can help identify loops.
- Clear Your Browser Cache: Sometimes, your browser may cache an old, incorrect redirect. Clear your cache and cookies to ensure you are testing the live version of your redirect rules.
Regularly auditing your redirects is a crucial maintenance task. By proactively identifying and fixing chains and loops, you can ensure a fast, reliable experience for your users and maintain a healthy relationship with search engines.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is HTML 301?
The term "HTML 301" is slightly misleading. A 301 redirect is an HTTP status code sent by a server, not an HTML element. However, the term is often used to refer to a client-side method that mimics a redirect using an HTML meta refresh tag (<meta http-equiv="refresh" ...>). This method is not a true 301 redirect and is considered less SEO-friendly than a server-side implementation.
2. How to redirect a URL in HTML?
You can redirect a URL using the HTML meta refresh tag placed within the <head> section of your page. To create an immediate redirect, set the content delay to "0": <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0; url=https://www.new-url.com/">. While this works, it is not the recommended method for permanent moves due to potential negative impacts on SEO and user experience.
3. How do I add 301 redirects to my website?
The best way to add a 301 redirect is at the server level by editing your .htaccess file (for Apache servers). If you use a CMS like WordPress, the easiest method is to use a dedicated redirection plugin. For website builders like Wix or Shopify, use their built-in URL redirect manager found in the site's settings or SEO tools.
4. Is 301 a permanent redirect?
Yes, a 301 status code explicitly means "Moved Permanently." It signals to search engines and browsers that the change in URL is not temporary and that they should update their records to the new location. This is why it's the correct choice for permanently relocating content, as it helps preserve your SEO rankings at the new address.